The execution of Ahmed Abdul Ali in Yemen highlights significant issues surrounding capital punishment, drawing attention from human rights advocates, legal professionals, and those concerned about the complexities of state-sanctioned death. This high-profile case unfolds within a backdrop of ongoing human rights violations, sparking outrage both domestically and internationally. As Yemen contends with political instability and a compromised judicial system, the legal processes leading to Abdul Ali’s execution illuminate broader themes of injustice, inadequate legal representation, and violations of international standards.
Understanding this case requires a detailed examination of the legal framework that permitted the execution, encompassing the specific charges against Abdul Ali, the trial procedures, and the observed fairness of these proceedings. Furthermore, by analyzing the societal repercussions of such executions, particularly the emotional toll on families and their communities, deeper insights emerge regarding the implications of capital punishment in a region rife with turmoil.
This article will explore the specifics of the execution process, the psychological ramifications for affected families and communities, the responses from human rights organizations, the ethical considerations surrounding capital punishment, and international efforts aimed at abolishing this practice. Each of these aspects contributes to a comprehensive understanding of the execution process and its societal impact.
What Led to the Execution of Ahmed Abdul Ali?
Ahmed Abdul Ali faced charges connected to accusations of involvement in anti-government activities under the Houthi regime. This situation serves as an entry point for understanding Yemen’s judicial landscape, where the rule of law has been increasingly undermined.
Reports indicate that trials conducted by Houthi courts routinely lack transparency and fail to uphold basic legal standards. Observers from international organizations, including the United Nations and Human Rights Watch, have condemned these procedures as egregious violations of human rights. For instance, Abdul Ali’s access to effective legal representation was questionable, with limited availability of professional counsel throughout critical phases of the trial.
In recent years, statistics have revealed troubling trends in Yemen’s capital punishment practices. Since 2014, Houthi authorities have sentenced numerous individuals to death, leading to significant concerns about due process. Reports indicate that 350 death sentences have been issued, with only 11 executions carried out. These figures not only underscore the urgent need for judicial reform but also impact societal perceptions of justice and human rights.
An image illustrating key court documents related to the execution of Ahmed Abdul Ali (Source: The New York Times)
Understanding the Psychological Impact of Executions on Society
The impact of executions, such as that of Ahmed Abdul Ali, reverberates profoundly through families, friends, and broader communities. Families of individuals on death row often experience intense emotional distress, living in a constant state of uncertainty and fear regarding the impending loss of their loved ones. In Abdul Ali’s case, his family encountered significant societal stigma and isolation, as families connected to executed individuals frequently face ostracism.
Reports from families of other individuals previously sentenced to death highlight patterns of psychological trauma. Many attested to the prolonged anticipation of an execution resulting in serious mental health issues. In certain instances, children of those facing execution are left without parental support, exacerbating the challenges posed by capital punishment.
In environments where executions are entwined with discussions on justice, communities often grapple with complex moral implications, leading to divisions and fervent debates about the ethicality of such measures. Additionally, these emotional effects extend beyond immediate families, disrupting community dynamics and altering perceptions of fairness and morality.
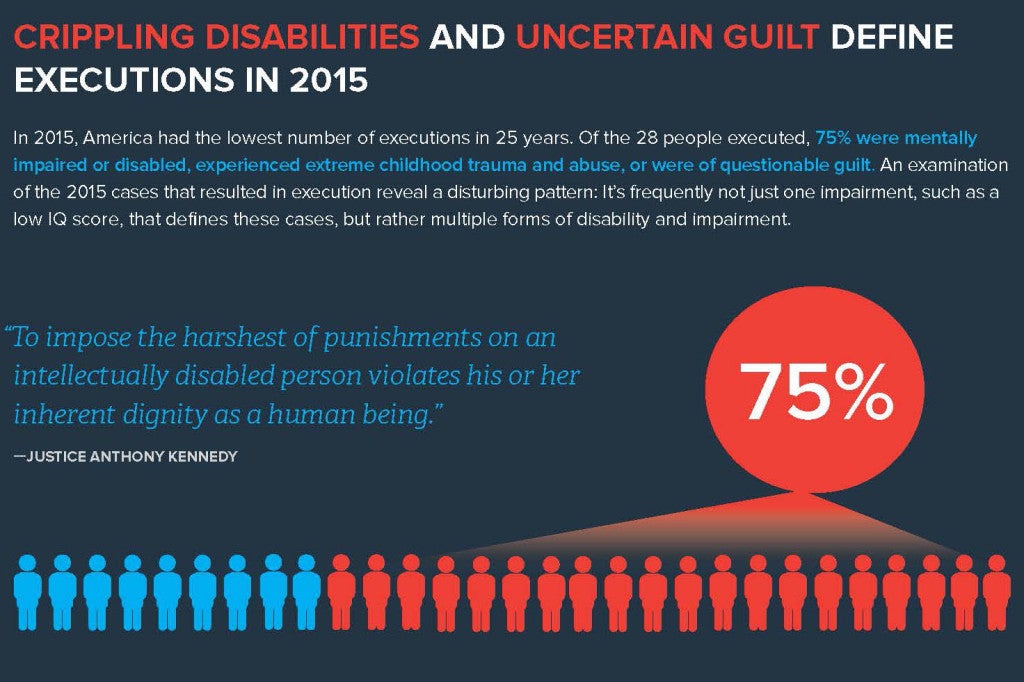
This infographic presents statistics on the mental health impacts of executions (Source: Harvard Law School)
How Executions Influence Human Rights Advocacy
The case of Ahmed Abdul Ali has catalyzed significant advocacy concerning the injustices related to capital punishment within Yemen. Human rights organizations, including Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch, have tirelessly worked to raise awareness of the violations entrenched in the Houthi-controlled judicial system. These groups not only condemn the practice of capital punishment but also the overarching conditions that sustain such practices.
Critics highlight that the existing legal frameworks governing capital punishment fail to guarantee fair trials. Reports from advocacy groups illustrate a growing public movement, including protests and campaigns pushing for the rights of those facing execution and advocating for systemic reforms to the judiciary. NGOs play an instrumental role in mobilizing international attention and garnering support for the abolition of death sentences, promoting legal representation for those accused.
International human rights law, including protocols aimed at halting the death penalty, emphasizes the collective responsibility of nations to uphold human dignity. The continued advocacy surrounding Abdul Ali’s case provides an essential platform for broader discourse on the necessary systematic reforms in Yemen and similar regions that utilize the death penalty.
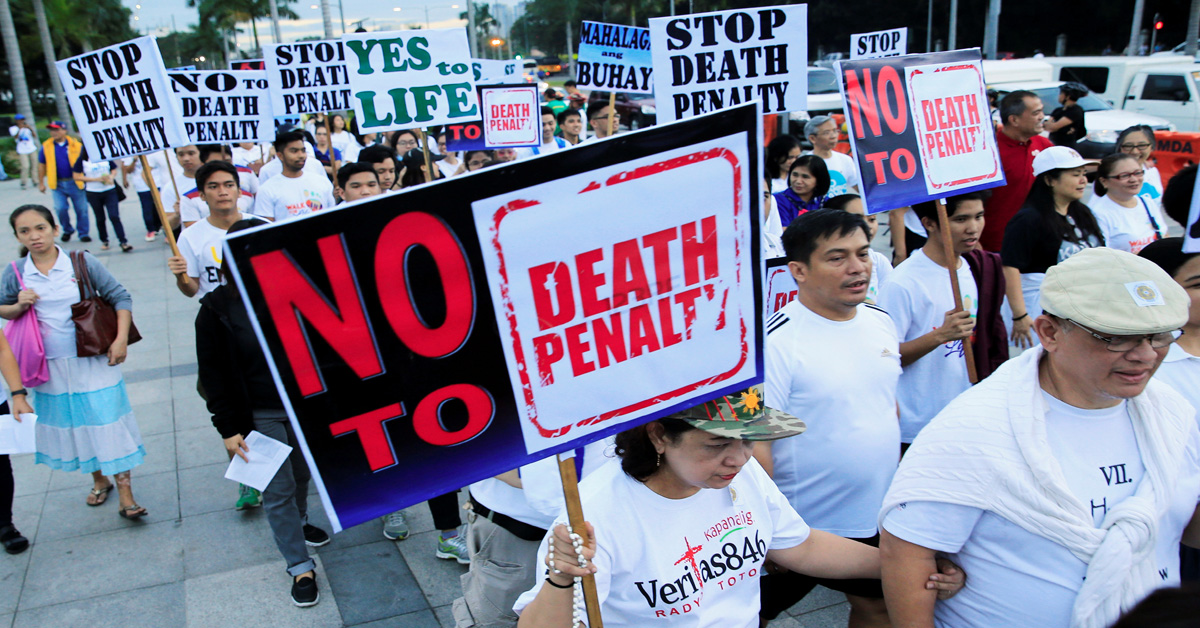

An image capturing a protest organized by human rights advocates against the death penalty (Source: Amnesty International)
Examining the Ethical Debate on Capital Punishment
The ethical implications of capital punishment remain contentious, particularly in relation to cases such as Ahmed Abdul Ali’s. Proponents of the death penalty often argue that it serves as a deterrent to violent crime, suggesting that the fear of execution may dissuade potential offenders. However, substantial counterarguments exist, emphasizing the lack of empirical evidence supporting deterrence claims.
Research reveals that regions without the death penalty frequently report lower murder rates than those that enforce capital punishment. This raises important questions about the effectiveness of the death penalty as a method for crime reduction and prompts ethical considerations regarding its use, particularly concerning wrongful convictions and irreversible judicial errors.
Additionally, the morality of executing individuals—often within legal systems lacking in due process—fuels ongoing debates regarding whether state-sanctioned death is a justified form of punishment. Ethical arguments predominantly center around the preservation of human life and the potential for rehabilitation as fundamental tenets in the opposition to capital punishment.

A diagram presenting various arguments for and against capital punishment (Source: IAS Toppers)
The Road to Abolishing the Death Penalty: Global Perspectives
International efforts to abolish the death penalty have gained traction, especially in light of notable cases like that of Ahmed Abdul Ali. The Second Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights aims for a global abolition of the death penalty, with 112 countries ratifying this protocol as of 2024.
Regional initiatives, particularly within Europe, have shown overwhelming success. The Council of Europe has made abolition a prerequisite for membership. Recent legislative actions in countries such as Zambia and Ghana signify positive developments toward ending capital punishment.
In stark contrast, Yemen’s judicial system struggles with ongoing challenges. The alarming statistics surrounding executions and the lack of transparency in trials necessitate urgent international intervention. As the global discourse around human rights continues to evolve, perspectives on capital punishment shape the attitudes and actions of nations contemplating reform.
A world map indicating the status of death penalty abolition across different countries (Source: Wikipedia)
Taking Action: How to Advocate for Change
Human rights advocates, legal professionals, and other concerned individuals can play a vital role in combating capital punishment while supporting families affected by such executions. Effective strategies for advocacy include educating communities about the realities surrounding capital punishment, fostering dialogues to challenge misconceptions, and utilizing social media to amplify voices against the death penalty.
Engagement with local and global human rights organizations offers essential resources and support for those seeking to raise awareness. Sharing experiences from families affected by executions often serves as a powerful motivator for change. Building coalitions among diverse groups can further amplify efforts and strengthen the advocacy for legal reforms.
Moreover, remaining informed about legislative developments enables advocates to respond proactively and actively participate in movements seeking to abolish the death penalty. As evidenced by the outcry resulting from the execution of Ahmed Abdul Ali, dedicated advocacy can significantly influence public opinion and government policy.

An image illustrating a guide for advocacy actions against capital punishment (Source: The Advocates for Human Rights)
Conclusion
The execution of Ahmed Abdul Ali underscores the urgent need for reforms in Yemen’s judicial system and a more profound comprehension of the ramifications of capital punishment on society. The connections between legal processes, psychological impacts, advocacy efforts, and ethical considerations create a complex landscape that advocates and legal professionals must navigate.
By fostering awareness, supporting advocacy, and promoting legislative reforms, individuals can significantly impact the global movement toward abolishing the death penalty. Through collaborative efforts, substantial change can be pursued, resulting in a more just and humane approach to punishment and an unwavering respect for human rights.




